India's journey toward becoming a global economic powerhouse is marked by remarkable achievements in its export landscape. The nation has demonstrated significant progress in diverse sectors, ranging from petroleum oils and agrochemicals to semiconductors and precious stones. This growth reflects India's ability to leverage advanced technology, innovative practices, and competitive manufacturing to meet global demands. Supported by robust government initiatives, the country is not only expanding its export base but also strengthening its position as a reliable global supplier. India's export performance in several key product categories at the 4-digit HS level has shown notable success, with the country maintaining or improving its rank among the top 10 global suppliers, all with export values exceeding $1 billion in 2023.
Below is a detailed exploration of India's robust performance in various key export categories, highlighting its advancements in global trade:

India has emerged as a dominant player in the global export market, showcasing remarkable growth across various sectors. The petroleum sector (Petroleum Oils and Oils Obtained from Bituminous Minerals) has seen a dramatic rise, with export values increasing from $60.84 billion in 2014 to $84.96 billion in 2023, capturing a global market share of 12.59%. This significant leap has propelled India to the position of the second-largest global exporter, driven by advanced refining infrastructure, increased production capacity, and adherence to international standards, solidifying its reputation as a dependable energy supplier worldwide.
In the agrochemical sector, India has achieved notable success, particularly in insecticides, rodenticides, and fungicides. By 2023, exports reached $4.32 billion, marking a global market share of 10.85%, up from 5.89% in 2014. Investments in research and development, coupled with compliance with international agricultural standards, have positioned India as the third-largest exporter globally. This growth underscores India’s pivotal role in supporting sustainable agriculture.
India’s sugar exports have also witnessed exceptional growth, with the country’s share in the global market for cane or beet sugar rising from 4.31% in 2014 to 12.21% in 2023. Export values reached $3.72 billion in 2023, cementing India’s position as the second-largest sugar exporter. Strong production bases and favourable agricultural policies have enabled India to cater to growing demand, particularly in Southeast Asia and Africa, strengthening its agricultural economy.
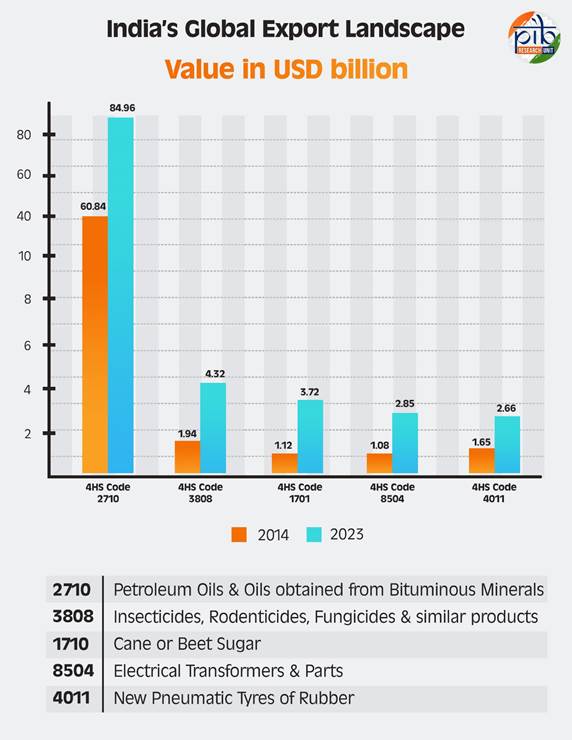
The electronics manufacturing sector has shown significant advancements, reflected in the exports of electrical transformers and related components, which grew from $1.08 billion in 2014 to $2.85 billion in 2023. India’s global market share increased to 2.11% in 2023, and it is in 10th position, up from 17th in 2014. Government initiatives such as "Make in India" and production-linked incentive schemes have bolstered this progress, creating a robust manufacturing ecosystem.
India has made remarkable strides in rubber pneumatic tyre exports, which reached $2.66 billion in 2023. Its global market share rose to 3.31%, securing the 8th position, a notable leap from 14th in 2014. This growth reflects India’s emphasis on quality, cost competitiveness, and the ability to serve diverse markets, particularly in emerging economies. Similarly, exports of taps, valves, and similar industrial products reached $2.12 billion in 2023, capturing a 2.16% global market share and earning India the 10th position globally. Advanced manufacturing processes and adherence to international standards have contributed to this success.
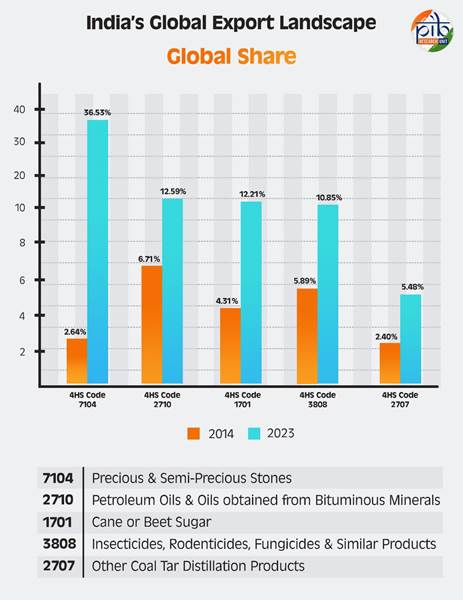
The country’s strategic focus on electronics and semiconductors has yielded impressive results. Exports grew from $0.23 billion in 2014 to $1.91 billion in 2023, achieving a global market share of 1.40% and securing the 9th position, a significant jump from 20th in 2014. This progress highlights India’s growing role in the global semiconductor supply chain, supported by efforts to enhance domestic manufacturing and innovation. Additionally, India’s exports of coal tar distillation products reached $1.71 billion in 2023, capturing a 5.48% global market share and securing 4th place globally showcasing its importance in industrial value chains.
In the export of precious and semi-precious stones, India has established itself as the world leader, with its global share surging from 2.64% in 2014 to an astounding 36.53% in 2023. Exports valued at $1.52 billion highlight India’s centuries-old craftsmanship and adoption of modern technology in gemstone processing. Exports of parts for electric motors and generators have also shown significant growth, reaching $1.15 billion in 2023, with a global share of 4.86%, elevating India to 6th place from 21 in 2014 globally. This growth aligns with the rising global demand for renewable energy and electric vehicle components, positioning India as a key supplier in this transformative industry.
Government Initiatives to Strengthen India’s Export Landscape
The Central Government has implemented various initiatives and policies to enhance exports, attract investments, and promote ease of doing business. A New Foreign Trade Policy was launched on March 31, 2023, and took effect on April 1, 2023. The policy's core approach is built on four key pillars: (i) Incentives for Remission, (ii) Export promotion through collaboration with exporters, states, districts, and Indian missions, (iii) Enhancing ease of doing business by reducing transaction costs and implementing e-initiatives, and (iv) Focus on emerging areas such as e-commerce, developing districts as export hubs, and streamlining the SCOMET (Special Chemicals Organisms Materials Equipment and Technologies) policy. It emphasizes emerging sectors like dual-use high-end technology under SCOMET, boosting e-commerce exports, and fostering collaboration between states and districts for export growth. The new Foreign Trade Policy (FTP) introduces a one-time Amnesty Scheme to help exporters clear old pending authorizations and start anew. It also promotes the recognition of new towns through the "Towns of Export Excellence Scheme" and acknowledges exporters via the "Status Holder Scheme."
To further support exporters, the Interest Equalization Scheme on pre- and post-shipment rupee export credit has been extended until August 31, 2024, with an allocation of Rs. 12,788 crores. Assistance is also being provided through schemes like the Trade Infrastructure for Export Scheme (TIES) and the Market Access Initiative (MAI).
To promote labour-intensive sector exports, the Rebate of State and Central Levies and Taxes (RoSCTL) Scheme has been in place since March 7, 2019, while the Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP) Scheme has been implemented since January 1, 2021. The RoDTEP Scheme was further expanded on December 15, 2022, to cover previously excluded sectors like pharmaceuticals, organic and inorganic chemicals, and iron and steel products. Additionally, anomalies in 432 tariff lines were addressed with revised rates effective from January 16, 2023. A Common Digital Platform for the Certificate of Origin has been launched to boost Free Trade Agreement (FTA) utilization by exporters.
The Districts as Export Hubs initiative identifies export-potential products in each district and addresses bottlenecks while supporting local exporters and manufacturers to generate employment. Indian missions abroad play an enhanced role in promoting India’s trade, tourism, technology, and investment goals. There is regular monitoring of performance involving with Commercial Missions abroad, Export Promotion Councils, Commodity Boards/ Authorities and Industry Associations, with corrective measures implemented as needed.
To attract domestic and foreign investments, the Government has introduced reforms such as the Goods and Services Tax (GST), corporate tax reduction, FDI policy changes, measures to reduce compliance burdens, and initiatives to boost domestic manufacturing through public procurement orders, the Phased Manufacturing Programme (PMP), and Quality Control Orders (QCOs). The Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Schemes for 14 key sectors, with an outlay of Rs. 1.97 lakh crore, aim to enhance manufacturing capabilities and exports.
The Government has prioritized simplifying, rationalizing, digitizing, and decriminalizing its interface with businesses and citizens across all States and UTs. Over 42,000 compliances have been reduced, and more than 3,800 provisions have been decriminalized. The National Single Window System (NSWS) allows businesses to apply for 277 Central approvals, with information on 661 approvals available through the Know Your Approvals (KYA) module. The Jan Vishwas (Amendment of Provisions) Act, 2023, promotes trust-based governance, decriminalizing 183 provisions under 42 Acts managed by 19 ministries and departments.
India’s roadmap for 2047 emphasizes global competitiveness, innovation, and integration into global supply chains. Policy reforms have improved India’s rank in the World Bank’s Doing Business Report from 142nd in 2014 to 63rd in 2019. Also, India’s rank in the Global Innovation Index (GII) amongst 132 economies has improved from 81st in 2015 to 40th in 2023. Intellectual Property Right (IPR) reforms have boosted patent grants from 5,978 in 2014-15 to 103,057 in 2023-24, while the number of designs registered grew from 7,147 to 30,672 during the same period.
The Startup India initiative, launched to foster innovation and entrepreneurship, has created a strong ecosystem, with 1.33 lakh DPIIT-recognized startups. Its action plan spans simplification, funding support, and industry-academia partnerships. Trade policy reforms have furthered India’s participation in global supply chains. The Foreign Trade Policy focuses on cost competitiveness, trade facilitation, and emerging sectors, provides a strong framework for promoting global supply chain participation.
On October 13th, 2021, the Government of India launched the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan to support infrastructure and social sector planning through the PM GatiShakti NMP GIS-enabled portal. The implementation of PMGS promotes multimodal connectivity, improves last-mile connectivity, and contributes to both Ease of Doing Business and Ease of Living. To complement the PM GatiShakti NMP, the National Logistics Policy (NLP) was introduced on September 17th, 2022 with the goal of reducing logistics costs and enhancing logistics efficiency across the country. Together, these policies are driving innovation and enabling greater integration with global supply chains.
The comprehensive Trade Connect e-Platform launch has successfully linked more than 6 lakh IEC holders, 185 Indian Mission officials, and over 600 Export Promotion Council members with the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT)/DoC offices and banks. This digital initiative improves the ease of doing business for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) by offering them valuable information and support, creating a more efficient and transparent export ecosystem. The government has rolled out Enhanced Insurance Cover for MSME Exporters to promote exports, which is expected to provide Rs. 20,000 crore in credit at reduced costs. This initiative aims to enhance the competitiveness of Indian exports and will benefit approximately 10,000 exporters.
The self-certified electronic Bank Realization Certificate (eBRC) system reduces compliance costs, saving exporters over ₹125 crore. This system also supports the government's broader objectives of fostering a digital, eco-friendly economy, reducing both administrative and environmental costs. The bulk generation and Application Programming Interface (API) integration of eBRCs streamline the process for exporters, especially small e-commerce businesses, by efficiently managing high-volume, low-cost transactions. This system helps them claim benefits and refunds more effectively, supporting their growth in international trade.
The E-Commerce Export Hub (ECEH) initiative aims to revolutionize India’s cross-border e-commerce, potentially reaching USD 100 billion in exports by 2030. These hubs connect SMEs, artisans, and One District One Product (ODOP) producers to global markets, boosting logistics efficiency and economic inclusion in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities. On the Government e-Marketplace (GeM), revised pricing slabs now cap charges at ₹3 lakh for orders above Rs. 10 crore, significantly reducing transaction costs. The Bharat Mart in Dubai provides Indian MSMEs affordable access to Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), African, and CIS markets, enhancing exports to these regions.
Jansunwai, a platform that facilitates direct communication between stakeholders and the Government, eliminating intermediaries and saving time. A revamped National Programme of Organic Production (NPOP) is set to benefit approximately 20 lakh farmers from 5,000 grower groups through enhanced export opportunities. It is expected to drive organic exports beyond USD 1 billion by 2025-26, benefiting approximately 20 lakh farmers.
ICEGATE (Indian Customs Electronic Commerce/Electronic Data Interchange Gateway) offers e-filing services to trade, cargo carriers, and other trading partners. Additionally, it provides facilities like e-payment, online registration for IPR, document tracking status at Customs EDI, online verification of DEPB/DES/EPCG licenses, IE code status, PAN-based CHA data, and links to various other key Customs-related websites and information. The platform also features a 24/7 helpdesk for trading partners.
These initiatives underline the Government’s dedication to expanding India’s trade and fostering inclusive development, positioning India as a global economic powerhouse by 2047.
Conclusion
India’s export achievements are a testament to its evolving manufacturing capabilities, strategic policies, and commitment to innovation. From dominating the global market in precious stones to making inroads in advanced sectors like semiconductors and electrical components, India’s export journey underscores its growing economic prowess. The government's forward-looking initiatives, such as the New Foreign Trade Policy, PLI Schemes, and many others, play a pivotal role in enhancing India’s competitiveness on the global stage. As India diversifies its export portfolio and strengthens its global presence, it is poised to achieve its vision of becoming a global economic power by 2047.
References
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2039117
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2057038
https://enquiry.icegate.gov.in/












